- All products
- Access
- Backhaul
- Surveillance
- Industrial applications
- Operators
- Rural connectivity
- Enterprise Wi - Fi
- Hotspot
The Best Long-Range Wi-Fi Router
Connectivity has become an inherent part of many facets of modern life. There is a handful of factors that can be attributed to the rise of this trend, but the overarching element at play here is the Internet. However, while most businesses claim that it was the power of social media and the possibilities of instant messaging that gave rise to this trend, but a deeper dive into this issue shows that it was actually the concept of empowerment.
Being connected means being empowered. It enables businesses to provide services online, to execute targeted advertising campaigns, to establish and maintain direct relations with clients and followers, and much more. The best part about this is its low cost—users gain plenty more opportunities for a much smaller investment. Considering the fact that connectivity is no longer a luxury, but rather a necessity (for the same reasons stated above), skipping on this is no longer an option when striving for success.
What better way to stay connected than to set up a wireless corporate network using long-range Wi-Fi routers and wireless access points. Such an option does not require any drastic infrastructural changes, involves minimal effort to set up and maintain, supports a significantly broader spectrum of end devices, and remains as functional as any wired network.
In the context of routers and access points for businesses, long-range translates into 50–150 meters, but can be greater with the right tech.
Uses. Despite the fact that most dedicated Wi-Fi routers are for indoor use only, deployment is by no means restricted to a few options. These devices can still be installed in a variety of different locations, under very specific circumstances, and serve a multitude of functions without any compromise to their performance. Long-range Wi-Fi routers are often grouped into two general categories:
Being connected means being empowered. It enables businesses to provide services online, to execute targeted advertising campaigns, to establish and maintain direct relations with clients and followers, and much more. The best part about this is its low cost—users gain plenty more opportunities for a much smaller investment. Considering the fact that connectivity is no longer a luxury, but rather a necessity (for the same reasons stated above), skipping on this is no longer an option when striving for success.
What better way to stay connected than to set up a wireless corporate network using long-range Wi-Fi routers and wireless access points. Such an option does not require any drastic infrastructural changes, involves minimal effort to set up and maintain, supports a significantly broader spectrum of end devices, and remains as functional as any wired network.
In the context of routers and access points for businesses, long-range translates into 50–150 meters, but can be greater with the right tech.
Uses. Despite the fact that most dedicated Wi-Fi routers are for indoor use only, deployment is by no means restricted to a few options. These devices can still be installed in a variety of different locations, under very specific circumstances, and serve a multitude of functions without any compromise to their performance. Long-range Wi-Fi routers are often grouped into two general categories:
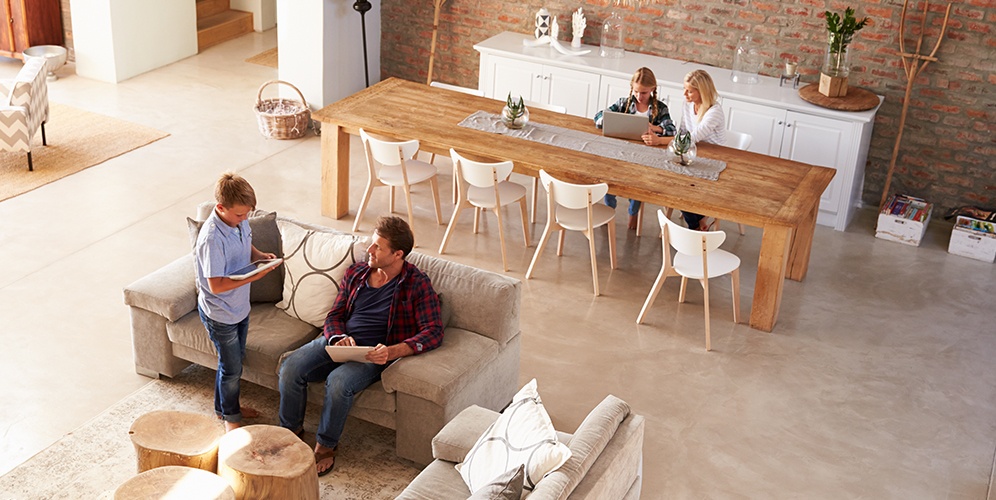
Home. Most households nowadays have Wi-Fi routers because of the immense popularity of mobile devices and laptops. Despite the commonness of short-range Wi-Fi routers, long-range models can also be found in certain households, especially large ones that have home offices.
Large homes take advantage of the capabilities of long-range Wi-Fi routers because a single device of such caliber can easily outperform 2–3 conventional home Wi-Fi routers. This means that less devices, less cables, and less space are required for a home network to function.
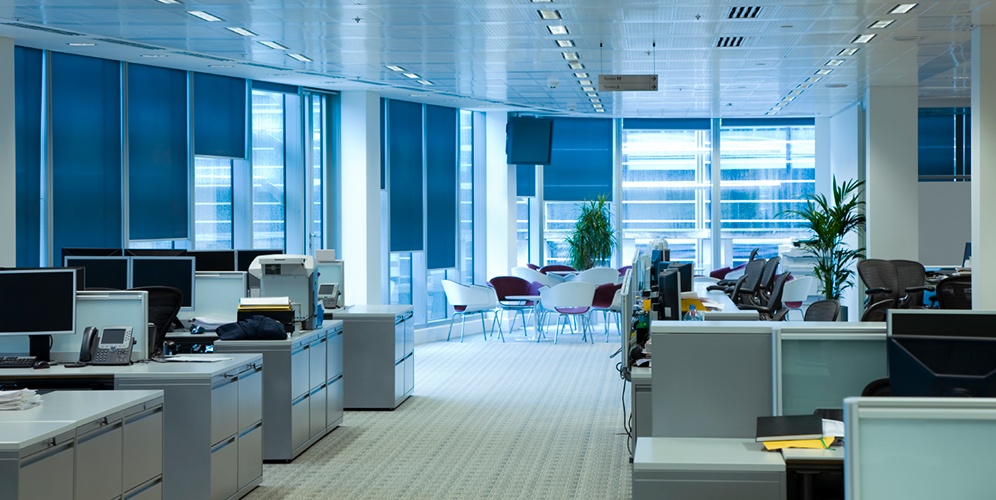


Business. Wi-Fi routers are prevalent in businesses for several reasons. Besides the fact that most companies have an online presence, thus requiring non-stop access to the Internet, businesses that receive a lot of visitors (such as coffee shops) also offer Wi-Fi to their patrons as an added service. To have a Wi-Fi router at a business means having a simple solution to managing a private network and possessing the tools to carry out analytics and marketing campaigns much more effectively.
Long-range Wi-Fi routers are an ideal solution for businesses because long-range models are generally more powerful than traditional routing equipment. This is especially useful as businesses require reliable performance and greater capacities at all times. This also makes expansion easier.
Long-range Wi-Fi routers can also be implemented to function in unconventional scenarios. The same technologies that deliver Internet to wireless devices can also be used to transfer video footage from surveillance cameras to a computer, connect telephone calls between neighbors, or support the performance of burglar alarm systems. The possibilities are virtually endless.
What Contributes to Long Range? There are a couple of factors that influence a router’s ability to deliver data over long distances. The following technical specifications should be considered when looking for the best long-range Wi-Fi router:
Frequency. A frequency is a waveband at which radio signals are transmitted. In the case of Wi-Fi, the most common frequency bands are 2.4GHz and 5GHz. However, Wi-Fi can function on other frequencies as well.
2.4GHz antennas deliver greater range, but 5GHz antennas function on significantly less-crowded channels and achieve greater throughput. Heavy-duty and long-range Wi-Fi routers typically utilize dual-band antennas to provide the best of both worlds.
Antenna Gain. Antenna gain is the ability to boost signal power by concentrating radio frequency energy in a specific direction or pattern. It complements the existing Wi-Fi router’s transmit power and significantly increases the range.
Conventional home Wi-Fi routers average at 2–4dBi, while long-range Wi-Fi routers deliver 5–9dBi gain. There are more powerful options and the general rule with antenna gain is the bigger—the better. However, having too much gain also causes greater noise levels, so sensibility is advised.
Transmit power is also a factor in increasing Wi-Fi router range. However, users should keep in mind that each country applies different transmit power and EIRP restrictions, so the adjustment of these values should be exercised with care and respect to the legal limits imposed by the national legislature.
What Contributes to Long Range? There are a couple of factors that influence a router’s ability to deliver data over long distances. The following technical specifications should be considered when looking for the best long-range Wi-Fi router:
Frequency. A frequency is a waveband at which radio signals are transmitted. In the case of Wi-Fi, the most common frequency bands are 2.4GHz and 5GHz. However, Wi-Fi can function on other frequencies as well.
2.4GHz antennas deliver greater range, but 5GHz antennas function on significantly less-crowded channels and achieve greater throughput. Heavy-duty and long-range Wi-Fi routers typically utilize dual-band antennas to provide the best of both worlds.
Antenna Gain. Antenna gain is the ability to boost signal power by concentrating radio frequency energy in a specific direction or pattern. It complements the existing Wi-Fi router’s transmit power and significantly increases the range.
Conventional home Wi-Fi routers average at 2–4dBi, while long-range Wi-Fi routers deliver 5–9dBi gain. There are more powerful options and the general rule with antenna gain is the bigger—the better. However, having too much gain also causes greater noise levels, so sensibility is advised.
Transmit power is also a factor in increasing Wi-Fi router range. However, users should keep in mind that each country applies different transmit power and EIRP restrictions, so the adjustment of these values should be exercised with care and respect to the legal limits imposed by the national legislature.
What Causes Best Performance?
Wi-Fi router range depends on more than just the hardware—the environment that it is placed in and the circumstances of the scenario are also significant factors. Consider these aspects when trying to achieve greater device range:
Physical Obstacles. Make sure any walls or objects that could potentially obstruct the link between the two wireless devices are kept to a minimum. Avoid placing the long-range Wi-Fi router near appliances such as microwave ovens as the radio waves emanating from them could cause a lot of interference when turned on.
Overloaded Channels. Sometimes long-range Wi-Fi routers cannot maintain strong links due to noisy and overcrowded channels. This is especially true with blocks of flats or office buildings where every individual household/company has its own wireless network. Switching to less used channels or enabling the auto-channel function helps to avoid this problem.
Bad Location. When deploying long-range Wi-Fi routers, users should look for a functional spot—not a convenient one. It is best to place the long-range Wi-Fi router as high as possible and in a location that would allow the router to cover the entirety of the premises without leaving any dead spots.
Physical Obstacles. Make sure any walls or objects that could potentially obstruct the link between the two wireless devices are kept to a minimum. Avoid placing the long-range Wi-Fi router near appliances such as microwave ovens as the radio waves emanating from them could cause a lot of interference when turned on.
Overloaded Channels. Sometimes long-range Wi-Fi routers cannot maintain strong links due to noisy and overcrowded channels. This is especially true with blocks of flats or office buildings where every individual household/company has its own wireless network. Switching to less used channels or enabling the auto-channel function helps to avoid this problem.
Bad Location. When deploying long-range Wi-Fi routers, users should look for a functional spot—not a convenient one. It is best to place the long-range Wi-Fi router as high as possible and in a location that would allow the router to cover the entirety of the premises without leaving any dead spots.

There are other factors that can potentially diminish Wi-Fi router range, but the above-mentioned problems are the most common ones and the topic of range improvement deserves a separate dedicated discussion.
Simplicity at its Finest. When it comes to wireless technologies, look no further than LigoWave. LigoWave develops high-performance long-range wireless devices with innovation, versatility, and affordability in mind. LigoWave’s NFT 3ac, one of the most successful devices within the Infinity series, is a high-performance wireless access point and router that transforms the way home and business wireless solutions are done.
The NFT 3ac is equipped with two simultaneous dual-band 3×3 MIMO 802.11ac radios that achieve throughputs of up to 1.75Gbps and reach multiple devices up to 150 meters away. Despite its sheer power, the NFT 3ac provides ultimate ease as it can be used right out of the box—just plug it in and the device is ready to go. Whether it is power, simplicity, or long range, the NFT 3ac can deliver.
Be Empowered. Over the decades, connectivity has become a fundamental requirement for business success. As the times continue to progress, its role will grow even greater. Regardless of the venture that the user decides to take part in, they should in any case make maximum use of the tools available to them—to set up connectivity using long-range Wi-Fi routers and wireless access points.
Simplicity at its Finest. When it comes to wireless technologies, look no further than LigoWave. LigoWave develops high-performance long-range wireless devices with innovation, versatility, and affordability in mind. LigoWave’s NFT 3ac, one of the most successful devices within the Infinity series, is a high-performance wireless access point and router that transforms the way home and business wireless solutions are done.
The NFT 3ac is equipped with two simultaneous dual-band 3×3 MIMO 802.11ac radios that achieve throughputs of up to 1.75Gbps and reach multiple devices up to 150 meters away. Despite its sheer power, the NFT 3ac provides ultimate ease as it can be used right out of the box—just plug it in and the device is ready to go. Whether it is power, simplicity, or long range, the NFT 3ac can deliver.
Be Empowered. Over the decades, connectivity has become a fundamental requirement for business success. As the times continue to progress, its role will grow even greater. Regardless of the venture that the user decides to take part in, they should in any case make maximum use of the tools available to them—to set up connectivity using long-range Wi-Fi routers and wireless access points.