The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is a measure that compares the signal level to the amount of noise present in the medium of transmission. The value is expressed in Decibel (dB).
The range of SNR may vary between 1dB and 30dB. The optimum SNR range is 18–30dB. 18dB is the minimum value at which the device can still operate and deliver relatively optimum performance. Values lower than 18dB can drastically reduce the performance.
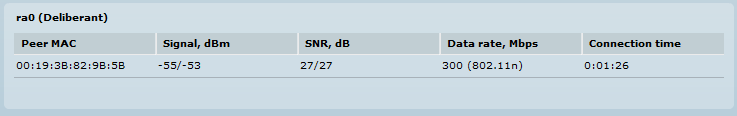
SNR is reported for each chain (V and H polarities). If only one antenna is connected, the reported SNR values will show up as 20/1 or 1/20. The maximum SNR value is 30dB, which indicates the best link quality. Anything that is above 18-20dB means that the link is working properly. Anything below those values may indicate that there is interference or that the selected settings are not suited for the current radio environment.
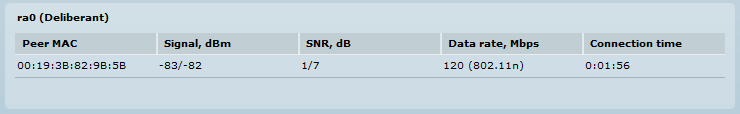
If one of the SNR values is equal to 1, it usually means that no data is passing through the second antenna’s polarity (this usually happens when there is no traffic present on the link) or when the RSSI is very bad on that polarity.
Example of a bad link quality and SNR: