Dynamic algorithm
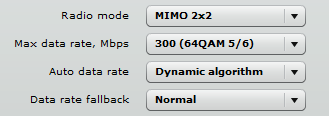
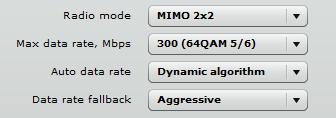
A dynamic algorithm (or auto data rate) is when a data rate is selected automatically by the mechanism that evaluates the performance of the device based on the current signal level, rate of data packet retry, and other relevant parameters.
Data rate fallback is the reduction of the data rate. When it is operating in Normal mode, it gradually reduces the modulation and coding scheme (MCS) until the data can pass through. When the data rate fallback is set to Aggressive, the MCS is decreased by 2 steps until it can pass the data through. The dynamic algorithm and aggressive fallback have to be used in noisy environments.
Fixed algorithm
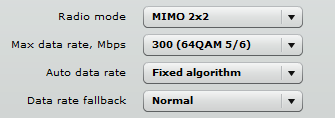
A fixed algorithm is when a data rate is a fixed value (MCS).
The main difference between the dynamic algorithm and the fixed algorithm is that the fixed algorithm will always try to send data under the selected MCS rather then decreasing the currently selected MCS to the value at which the retry rate is lower.
The fixed algorithm does not take into account signal level or the amount of retried packets. The data rate is only decreased when the device cannot send the current data at the fixed data rate. The data rate fallback mechanism turns on in such a case.
Data rate fallback operating in Normal mode gradually reduces the MCS until the data can pass through. When the data rate fallback is set to Aggressive, the MCS is decreased by 2 steps until it can pass the data through. A fixed data rate is best suited for operation in clean radio environments.